Contents
How to Position Your Brand Using Perceptual Maps
Perceptual maps are very helpful for determining an appropriate competitive strategy, depending upon the brand’s positioning.
There are some strategic approaches to using perceptual maps, such as:
- Looking for market gaps
- Crowding a competitor
- Repositioning a brand
- Repositioning a competitor
- Adopting a me-too positioning
Please note that example perceptual maps for each of these strategies are outlined below.
Looking for a Market Gap
The most common strategic use of a perceptual map involves looking for gaps in the market. These gaps may represent opportunities because no other firm/brand is perceived to be offering the same mix of benefits and features.
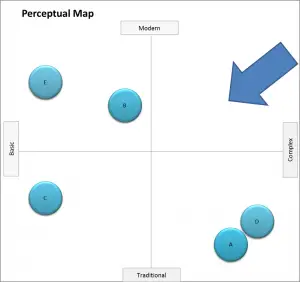
As highlighted in the following perceptual map, the arrow highlights a significant market gap, where there are no competitors perceived to be offering a brand/product that is both modern and more complex (that is, having many technical features).
This gap may or may not be viable. A viable market gap requires sufficient market demand (consumer need) along with the firm’s ability to access the market as well as requiring a suitable profit margin per unit.
For more information:
- How to Choose Attributes for a Perceptual Map
- Benefits of Perceptual Maps
- Top 12 Tips for Analyzing Perceptual Maps
Crowding a Competitor to Gain Market Space
There are many other strategic options to consider than just looking for gaps in competitive offerings. This is because this approach is simply too passive and too co-operative, particularly for large brands.
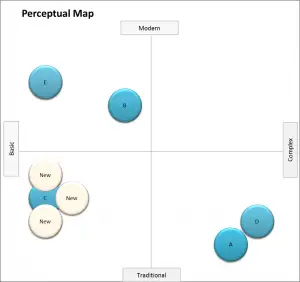
In the following perceptual map, a firm has made a strategic decision to take over a market position and has launched several brands. As a consequence, it is likely that existing competitor may need to consider repositioning their own brand.
For more information:
Repositioning a Brand
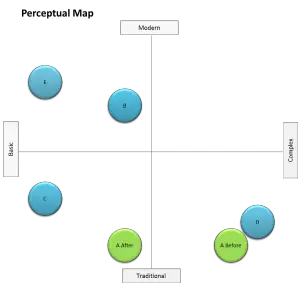
If a firm has attempted to reposition one of its brands in the minds of consumers, then it is very important to track how effectively this goal has been implemented.
To achieve this, we need to map the consumer’s understanding of each of the competitive brands at two points in time – typically before and after a major promotional campaign. We should find that the perception of all of the brands will move slowly over time. However, in the following perceptual map, only the repositioned brand is highlighted.
(You are able to use the free Excel template to show repositioned brands over time.)
For more information:
- Why and How to Reposition a Brand?
- Five Ways to Reposition a Brand
- Successful Repositioning Examples
- Unsuccessful Repositioning Examples
Repositioning a Competitor
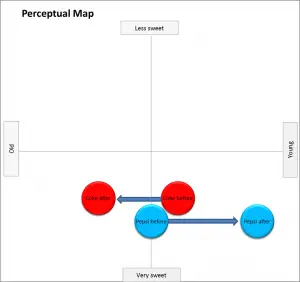
This is a much harder strategy goal because you have to almost reinvent two brands (yours and the competitor) through the one promotional campaign. However, it can be done. Two famous examples of this are Pepsi’s “choice of a new generation” slogan and Avis with their “we try harder” slogan.
In the first example of Pepsi, which is shown simply in the following perceptual map, Pepsi’s appeal to the youth market (the new generation) effectively repositioned Coca-Cola as “old and tired”. Likewise, the Avis campaign had the effect of positioning the market leader as having poor customer service.
For more information:
- Pepsi and Coke Positioning in the Cola Wars
- New Coke: Designed to Win Back Positioning
- Example Perceptual Maps for Soda (Soft Drinks)
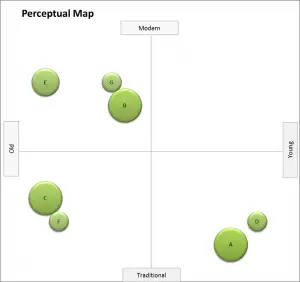
Adopting a me-too positioning
The complete opposite of looking for a gap in the market is to try and position very closely to a market leader. This is a relatively common marketing strategy for smaller brands. By aligning their brand name, packaging, colors and product design as closely as possible to a major player, the brand hopes that they will pick up some market share. Their goal is for either consumers to confuse the two brands or to perceive that the two brands are quite similar. And as the me-too brand tends to be quite price competitive, it should achieve a reasonable sales volume, particularly from budget-conscious shoppers.
This me-too positioning situation is highlighted in the following perceptual map. In this case, note that the circles vary in size; the larger the circle, the larger the brand’s market share. The smaller circles represent the me-too brands.
Quick FAQs for Using Perceptual Maps to Craft Brand Positioning
How can perceptual maps help determine a competitive strategy?
Perceptual maps provide valuable insights into the positioning of brands in relation to each other. This information can guide businesses in identifying market gaps, crowding competitors, repositioning their own brand, repositioning competitors, or adopting a me-too positioning strategy.
What is the strategic approach of looking for market gaps?
Looking for market gaps involves identifying areas where no competitors are perceived to be offering a similar mix of benefits and features. These gaps can present opportunities for brands to introduce products or services that meet unmet consumer needs.
How can crowding a competitor be a strategic approach?
Crowding a competitor means launching multiple brands in a specific market position to dominate that space. By crowding a competitor, a company can make it more challenging for existing competitors to maintain their brand position, potentially forcing them to consider repositioning their brand.
What is meant by “repositioning a competitor”?
Repositioning a competitor is a challenging strategy that involves attempting to change the perception of both your own brand and a competitor’s brand through a single promotional campaign. This strategy aims to position the competitor as less desirable or inferior compared to your brand.
What is me-too positioning?
Me-too positioning is a strategy where a brand closely aligns itself with a market leader, adopting similar brand names, packaging, colors, and product designs. The goal is to capture some market share by either confusing consumers or creating the perception of similarity with the dominant brand.
Why do smaller brands often adopt me-too positioning?
Smaller brands often adopt me-too positioning because it allows them to leverage the success and reputation of a market leader. By closely resembling the dominant brand, smaller brands hope to attract budget-conscious consumers and gain a reasonable sales volume.
Related Topics and Information
- What’s the difference between a perceptual map and a positioning map?
- Perceptual Maps: Best Practice
- How to Get the Most Out of Your Perceptual Maps
- Different Types of Perceptual Maps
- Free Download of the Perceptual Map Template
